
The Journal of Scientometric Research (J. Scientometric Res.) is the official journal of Phcog.Net. The open-access journal publishes peer-reviewed articles after carefully selecting them through a double-blind peer-review process. It encourages the development of scientometric research (in its broadest sense) as well as the use of scientometric data as ‘object of investigation’ or scientometric analysis in innovation and STS studies. It also reaches out to scholars of STS, sociology, economics, and related fields.
JCR Impact Factor in 2025 is 0.9
CiteScore in 2025 is 1.4
Frequency: Rapid at a time publication – Triannual (3 issues/year). Special issues are also published on contemporary areas from time-to-time.
Contents:
ABSTRACT
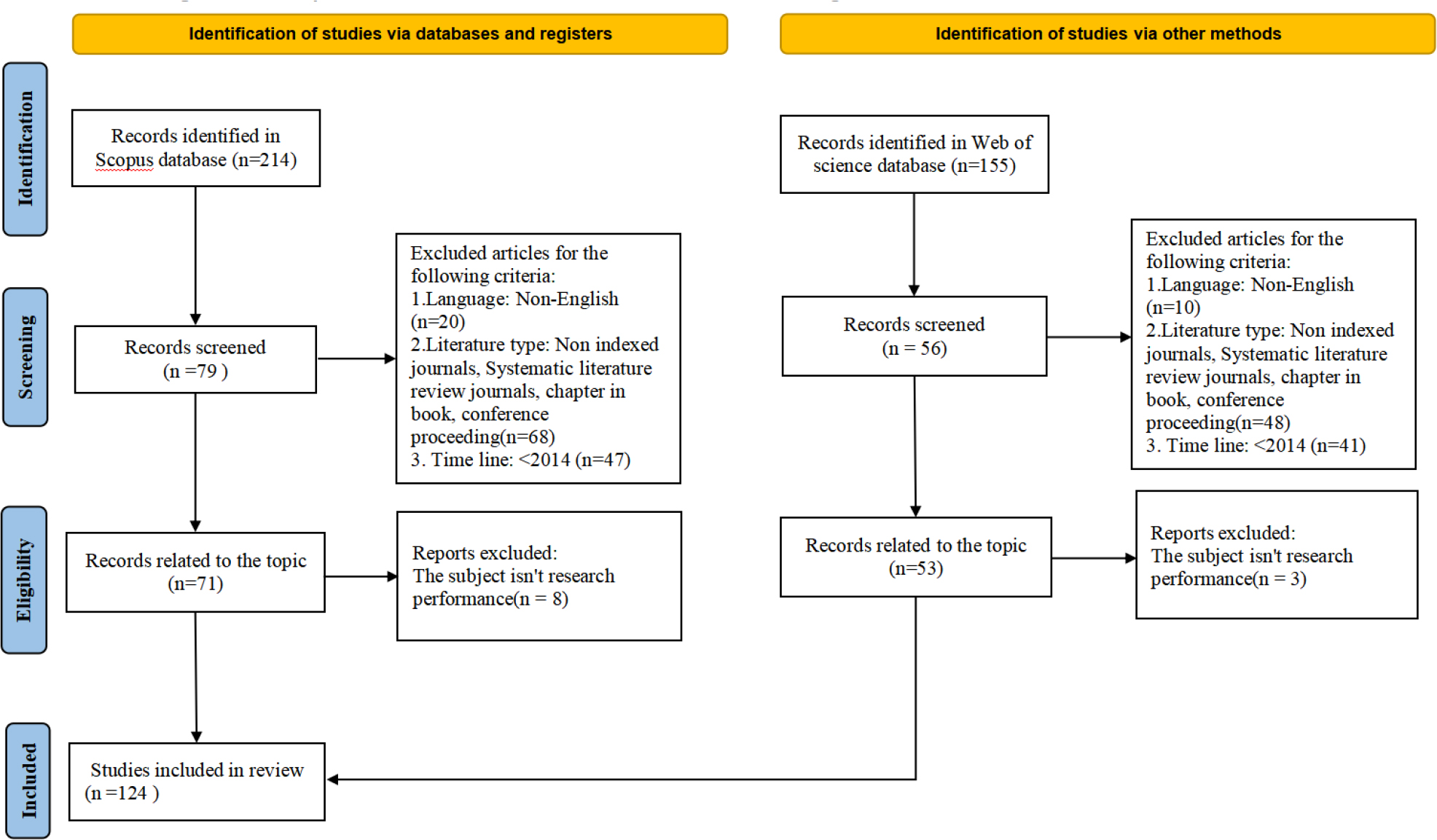
Under the background of globalization and the knowledge economy, scientific and technological innovation is of vital importance for enhancing a country's scientific and technological innovation capacity, strengthening its comprehensive national strength and international competitiveness. This article aims to comprehensively summarize the existing research on scientific research performance evaluation and explore the methods and influencing factors. For this purpose, this article adopts the PRISMA method to systematically review 76 articles on scientific research performance evaluation published from January 2014 to December 2024. The research finds that, first of all, the quantitative research method is the most often used approach, followed by the qualitative research method, while the mixed research method is the least frequently utilized. Second, research performance evaluation indicators are diversifying, with researchers no longer relying just on publications as a criterion. Instead, they are placing more emphasis on factors such as collaboration between research teams, international cooperation, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Third, the research performance is influenced by researcher’s academic proficiency, research interests, academic standing, work ethic, and career stage. Fourth, current academic circles tend to be result-oriented in research performance evaluation while neglecting the importance of process management and dynamic evaluation. This article comprehensively summarizes the research methods and their influencing factors in this field and provides insights for future research. Furthermore, this study also provides a reference for the scientific research achievements of research institutions to achieve sustainable economic growth and development.
ABSTRACT
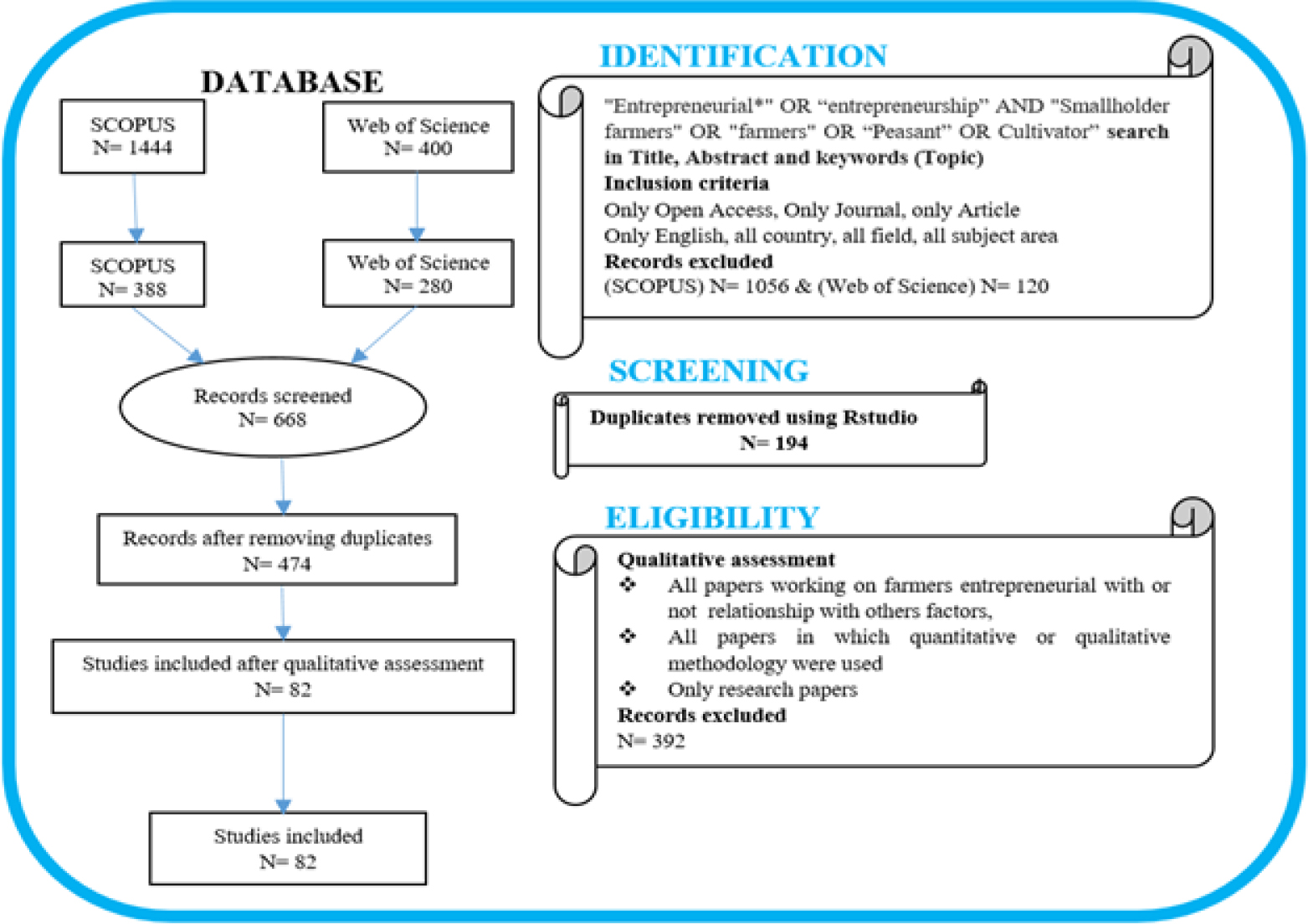
Global population growth has led to a rise in food consumption, placing increasing pressure on the agriculture sector to meet this demand. Despite advances in technology, smallholder farmers continue to face financial challenges. Researchers studied farmers' entrepreneurship to address this issue and boost farmers' income. This systematic literature review aims to comprehensively examine the existing body of research about the domain of farmers' entrepreneurship. The review used the PRISMA method to collect the requisite data from reputable database sources, including Scopus and the Web of Science. The study primarily focused on 82 open-access research papers in scholarly journals. A bibliometric analysis was conducted to explore content and network patterns, followed by a thematic analysis of the selected papers. The findings present the application of various entrepreneurial theories in agriculture, highlighting the interplay between farmers' internal traits (intention, resourcefulness) and external factors (market, technology, policy). The reviewed papers employed a range of advanced analytical techniques. It also found that entrepreneurial traits help farmers respond to market changes and customer needs. Additionally, these traits help them adopt soil-specific farming strategies, new seed varieties and technical developments in agricultural operations. Entrepreneurial policies mostly favor large-scale and professional farmers. However, smallholder farmers struggle to capitalize on entrepreneurial opportunities. The review highlights a gap in the literature regarding the entrepreneurial mindset, knowledge and aspirations of farmers and the impact of government support and existing facilities on smallholder farmer sustainable entrepreneurship. Future research should focus on understanding the enabling factors that help farmers adapt and thrive in the evolving agricultural landscape.
ABSTRACT
The landscape of publication of research papers is becoming more and more challenging, especially in terms of the financial, temporal, and ethical aspects. These challenges are made worse by the expanding power of accrediting bodies and technological advancements like Artificial Intelligence (AI). Article Processing Charges (APCs) sometimes exceed the financial means of academics and researchers, especially in developing and underdeveloped countries. High submission volumes and peer-review bottlenecks cause lengthy publication timelines, which further complicate matters and cause uncertainty and delays in scholars’ career advancement. Academic integrity is threatened by ethical issues like the improper use of AI tools, which also call into question the originality and creativity of research. This review draws upon insights from a curated body of recently published research papers to highlight structural injustices in academic publishing, their adverse effects on global research output, and the excessive pressure placed on faculty members to fulfill the requirements of accreditation agencies. To promote a more just and sustainable research ecosystem, this study suggests doable solutions, such as reforms in publishing economics, expedited peer-review procedures, and responsible AI use.
JEL Codes: D63, F63, I23, O33.
ABSTRACT
Solar cells, a crucial renewable energy source in the fight against climate change, have gained prominence in the scientific community. Sunlight, an almost inexhaustible source of clean and renewable energy, positions solar cells as a fundamental alternative for future energy needs. However, improving their energy efficiency remains a major challenge. Quantum dots, nanocrystals with unique properties, have emerged as a promising solution due to their ability to harvest a wider range of light wavelengths. Despite challenges in producing these cells, computational simulation tools based on Density Functional Theory (DFT) offer a robust theoretical framework. These tools provide a low-cost way to elucidate the internal processes of energy conversion, thereby accelerating development. The existing literature on this topic is scarce and dispersed, underscoring the need for research to consolidate key contributions. This article employs scientometric techniques to identify seminal works and analyze the dynamics in the scientific production of quantum dot-based solar cells. The results reveal a surge in research activity, particularly in the last three years, highlighting the growing interest in this promising technology. Moreover, results show a 38.95% growth between 2012 and 2019, with an upward trend in scientific production. China and the United States of America lead academic production in this field. Three well-defined trends in the development of quantum dot-based solar cells are identified: Halide perovskites, dye-sensitized, and nanocrystals. These findings can assist researchers in gaining a better understanding of the current research landscape and trends in this field.
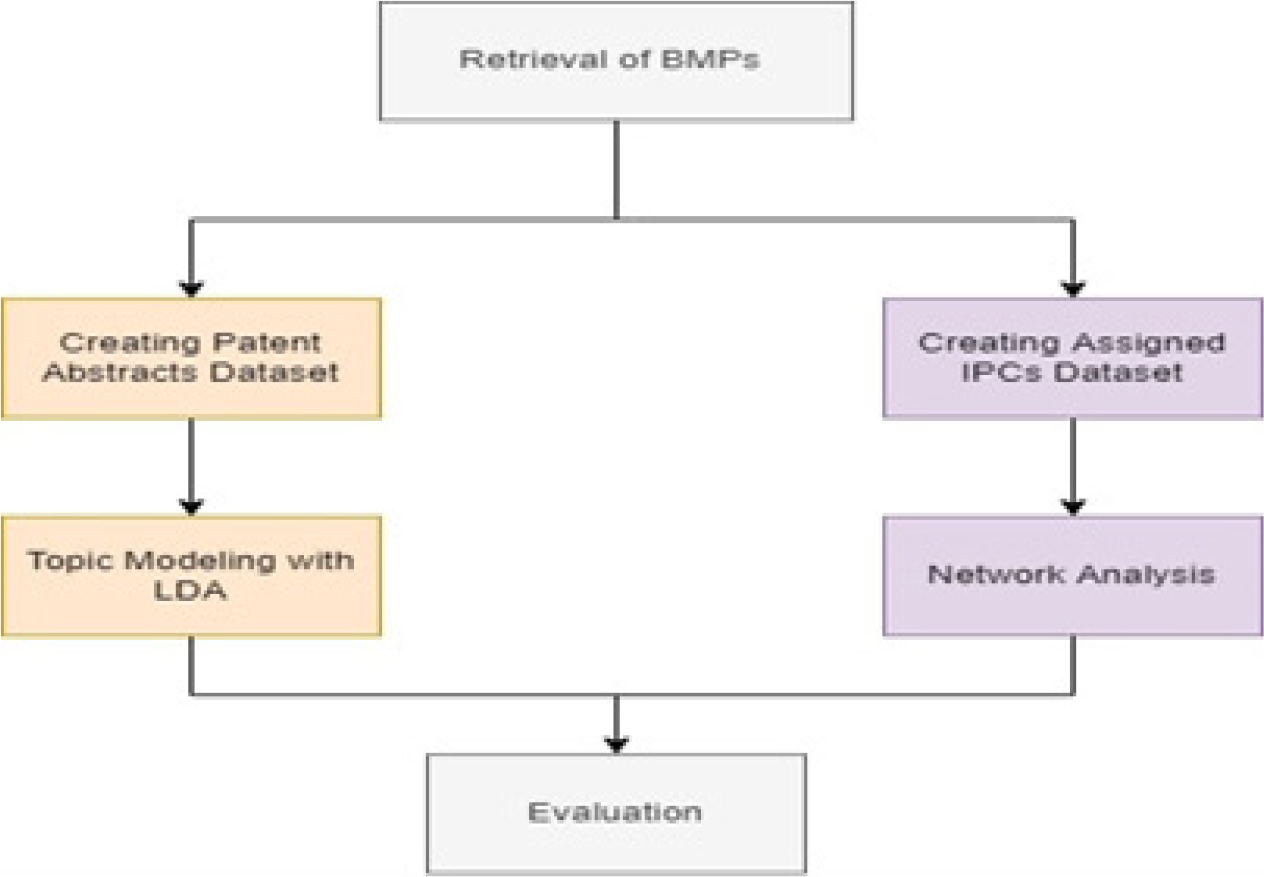
ABSTRACT
Business Method Patents (BMPs) have been a considerable option for companies to get a competitive advantage in the market. This paper focuses on the BMP applications filed to the Turkish Patent Office within a certain time frame in order to reveal the recent trends and potential inter-relationships with technology fields by topic modeling with Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and International Patent Classification (IPC) network analysis approaches. For topic modeling operation, the abstracts of the BMPs are used while attributed IPCs for those BMPs are the main anchors for the IPC network configuration. The findings on the final dataset containing 897 BMP applications show that active applicants persistently include technical characteristics of their industrial domain in their BMPs. That behavior consequently causes the BMP trends to shift into the main fields of those proprietors.
ABSTRACT
In recent years, supply chain instability has intensified due to increasing demand fluctuations, supply disruptions, and transportation interruptions, resulting in continuous volatility in production and operations. To effectively manage external disruptions, manufacturing firms are compelled to adopt flexible operational strategies. The concept of smart and flexible manufacturing has become more critical than ever, offering a key solution for enterprises to enhance their responsiveness to market volatility. Leveraging industry 4.0 technologies, smart-Flexible Manufacturing Systems (Smart-FMS) have emerged as a key solution to mitigate these challenges and ensure business continuity. Smart-FMS enables manufacturers to adapt to fluctuating demand, produce customized products, and address supply chain disruptions. This study offers a comprehensive review of Smart-FMS in the context of disruptions, using keyword cooccurrence analysis, thematic mapping, and thematic evolution analysis. By conducting a structured literature review and bibliometric network analysis of 1,764 research articles from the Scopus database (1965-2023), the study identifies emerging trends, prominent research areas, and future avenues of Smart-FMS. The findings provide valuable insights for manufacturers, engineers, and researchers seeking to implement or refine Smart-FMS in uncertainty environments, ultimately contributing to a more responsive and adaptable manufacturing industry.
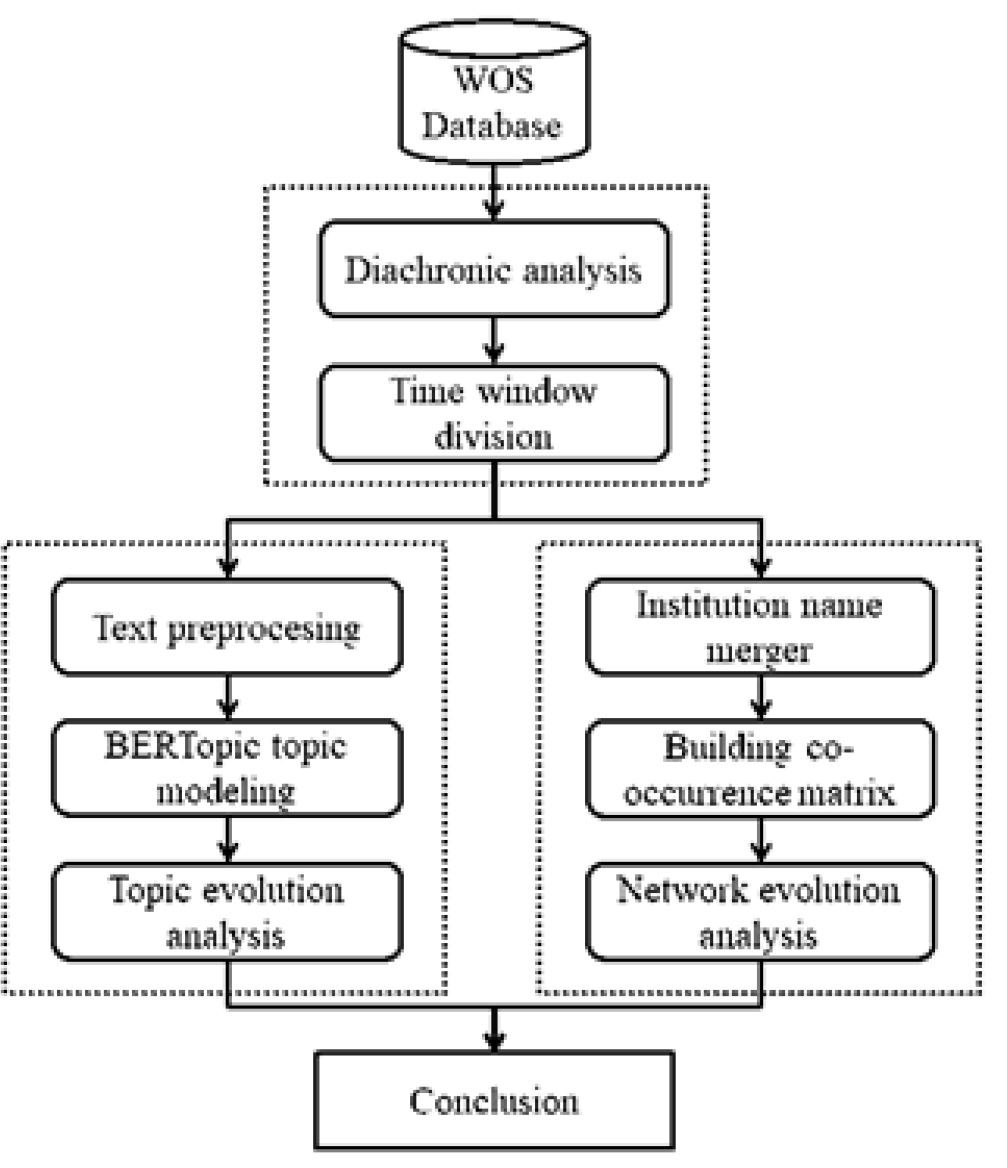
ABSTRACT
With the increasing demand for finer granularity in patent analysis, some scholars have started to explore the application of SAO (Subject-Action-Objection) triples to provide systematic descriptions of "problem-solution" in patent texts at a granular level. To investigate the progress in this field of research and assist scholars in identifying research topics and important research teams, this study utilizes the Web of Science database to retrieve academic papers in this domain. The study applies the BERTopic model and Gephi software to analyze the evolution of research topics and core research institutions in this field. The findings of this study reveal that the overall research in this field is in its preliminary exploration stage. Currently, scholars primarily focus on the application of SAO at the methodological level, and a stable core research group has not yet formed in this field. Future research should consider incorporating semantic associations between the Subject (S) and Objection (O) and expand the application of SAO triples to the theoretical level. Moreover, research teams in this field should actively seek collaboration and exchange to promote the advancement of SAO application research in patent analysis.
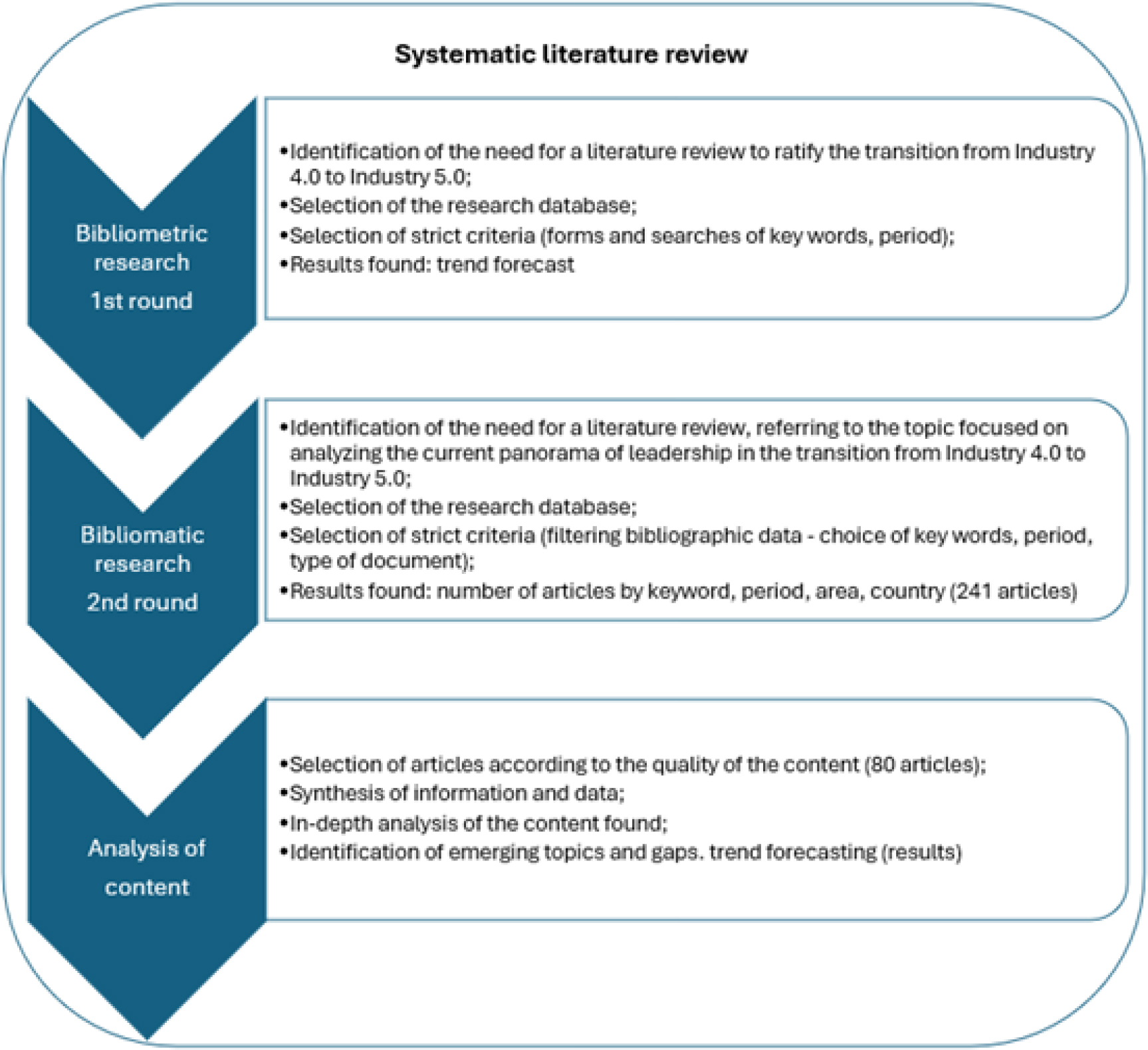
ABSTRACT
The objective of this article is to present a systematic review of the literature on leadership in the transition from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0 and to highlight potential for future research. A bibliometric and content analysis of a wide range of scientific production was carried out in order to present the main trends and critical points of this subject. Through the evaluation of a sample group of two hundred and forty-one articles, it was possible to trace paths and understand approaches, identifying features, highlights and challenges of the Industry 5.0 leader. The literature analyzed shows that this leadership is mainly based on the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary for performance and overcoming difficulties inherent to the demands of the industrial segment, which involve technological transformation, sustainability, resilience and human factors. This study fills a gap in the Industry 5.0 leadership literature by systematically exploring human-machine collaboration and sustainability-oriented leadership traits. Additionally, in addition to discussing how to address the demands inherent to Industry 5.0, this paper highlights that the consolidation of the transition from I4.0 to I5.0 is indeed in progress. In this scenario, this paper provides reflections for organizations that are experiencing this transition process.
ABSTRACT
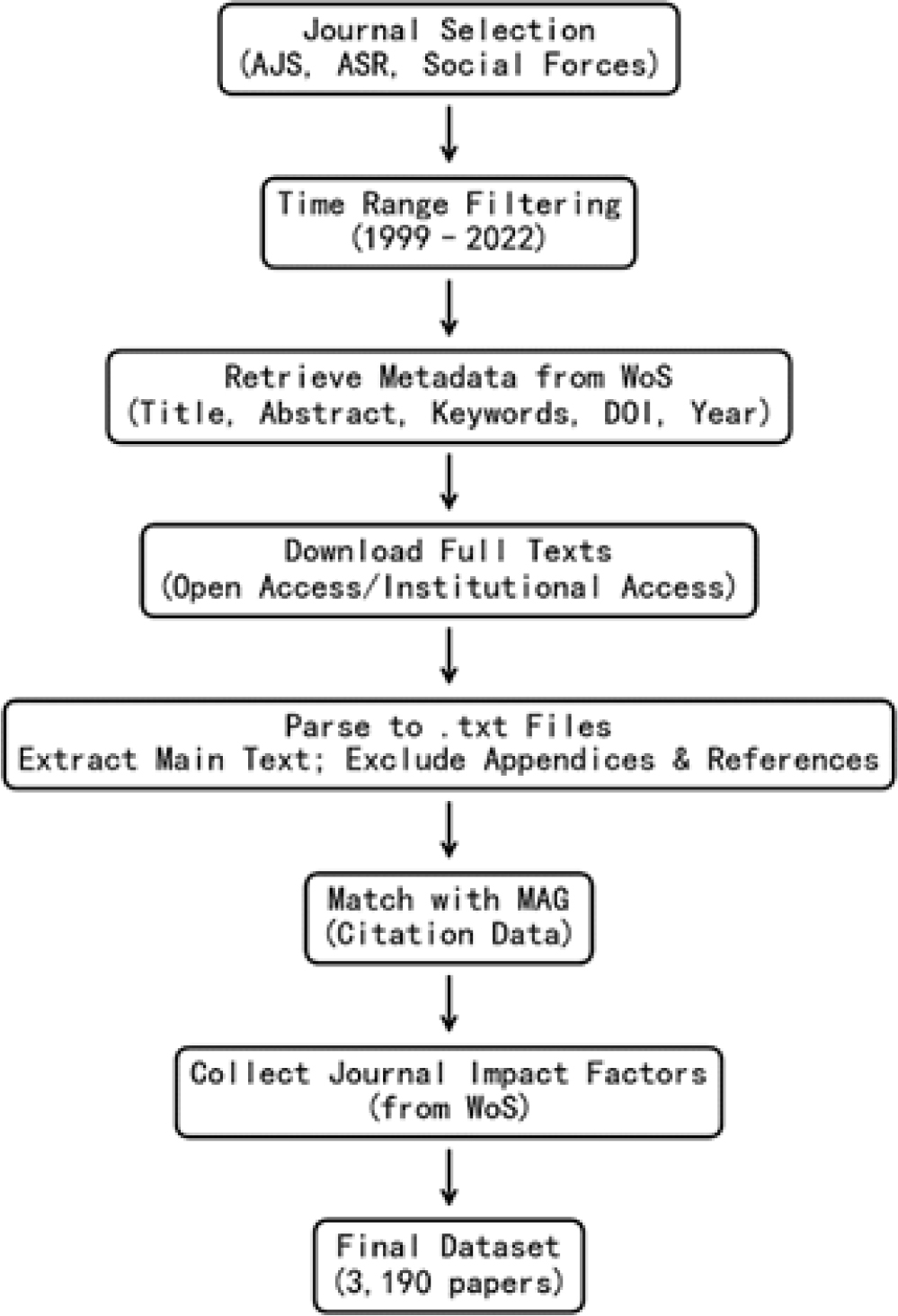
Why do papers of seemingly comparable quality generate widely different levels of scholarly impact? This study addresses this unresolved question by examining internal knowledge characteristics that may explain citation disparities among articles published in three top sociology journals between 1999 and 2022. Drawing on bibliometric techniques, we analyze a dataset of 3,190 articles using Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) to extract topic-based representations of each paper. We construct measures of context novelty, content novelty, and knowledge focus, and employ OLS regression models to assess their relationship with five-year citation counts. The analysis was conducted using Python. Contrary to prior findings, novelty measures fail to significantly predict citation outcomes when journal-level prestige is held constant. In contrast, knowledge focus-indicating the thematic concentration of a paper-shows a robust and consistent positive association with citation counts, suggesting that cognitive coherence may enhance scholarly visibility even in structurally comparable settings. This study contributes to ongoing debates about what drives scientific recognition by shifting the focus from external prestige signals to internal cognitive features. It also demonstrates the value of analyzing impact variation within similarly ranked journals-a context often overlooked in large-scale citation studies. The study is limited to the field of sociology, and does not account for factors such as network embeddedness or institutional affiliation. Future research could apply similar designs to other disciplines and incorporate additional contextual variables.
ABSTRACT
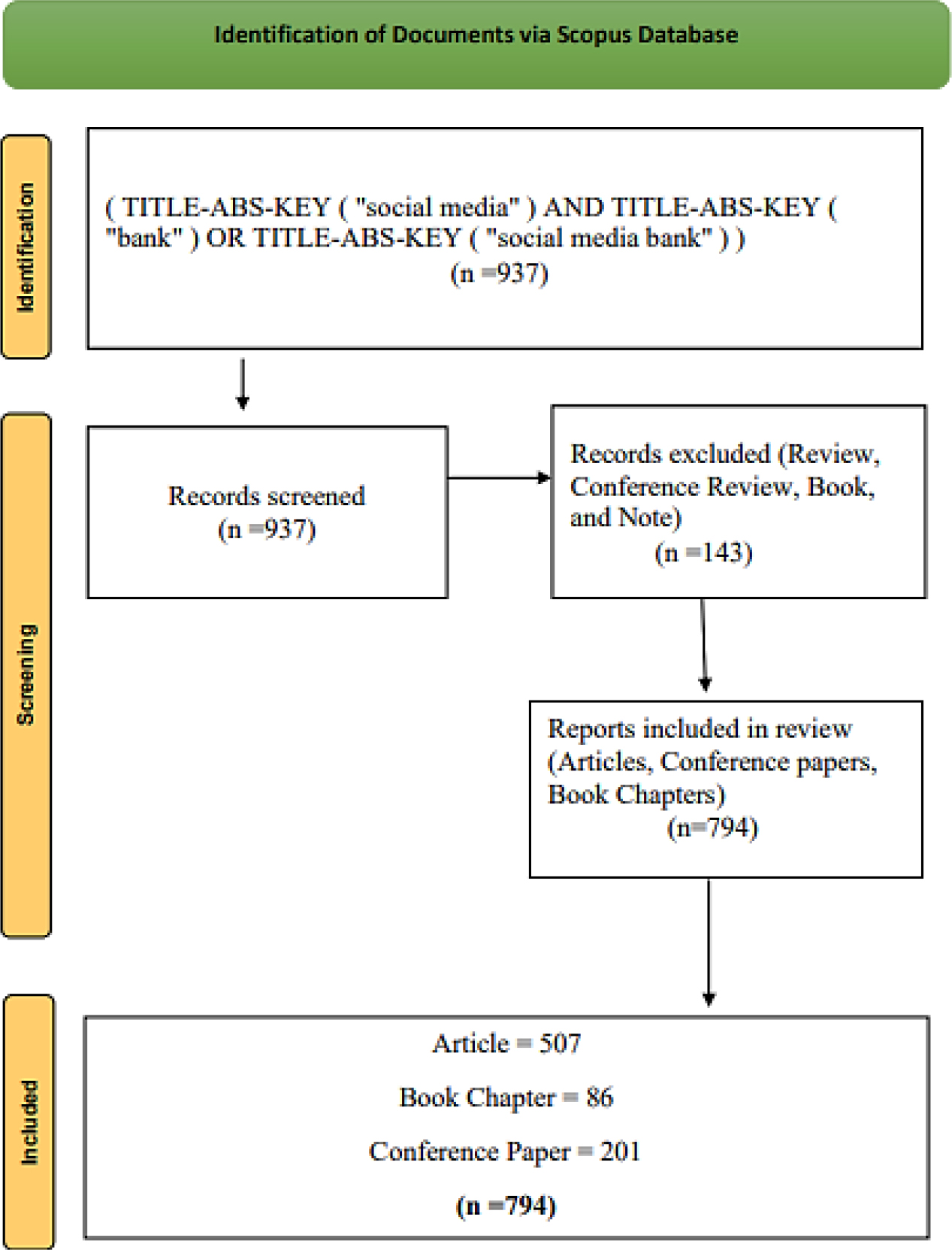
This bibliometric study explores the burgeoning field of social media banking, which merges banking services with social media platforms to facilitate customer access to financial services. Utilizing Scopus as the source for bibliographic data and adhering to PRISMA guidelines for document selection, the analysis employs bibliometric software tools such as Biblioshiny, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace to visualize and analyze key trends, themes, and influential contributors from 2007 to 2024. The study reveals significant annual growth in scientific production, with 2,494 authors contributing 794 documents, averaging 8.69 citations each. Prominent research clusters include the intersection of social media and banking, such as security, sentiment analysis, customer engagement, blockchain, and fintech. Citation bursts for keywords like "internet banking" and "social networking" indicate shifts in scholarly interest. Furthermore, the study identifies the most relevant authors, sources, and globally cited documents, while also exploring current trend topics, a thematic map, and bibliographic coupling. Visualizations like the co-occurrence of keywords and topic dendrograms provide deeper insights into developing themes and research connections. Notably, the role of social media platforms in banking has spurred extensive research into corporate reputation management, CSR communication, and financial technology. The study also highlights research gaps and practical implications, suggesting that banking institutions can innovate by leveraging social media strategies to enhance user experience and trust. In summary, the findings outline emerging opportunities and gaps, pointing to areas for future research and development in social media banking.
ABSTRACT
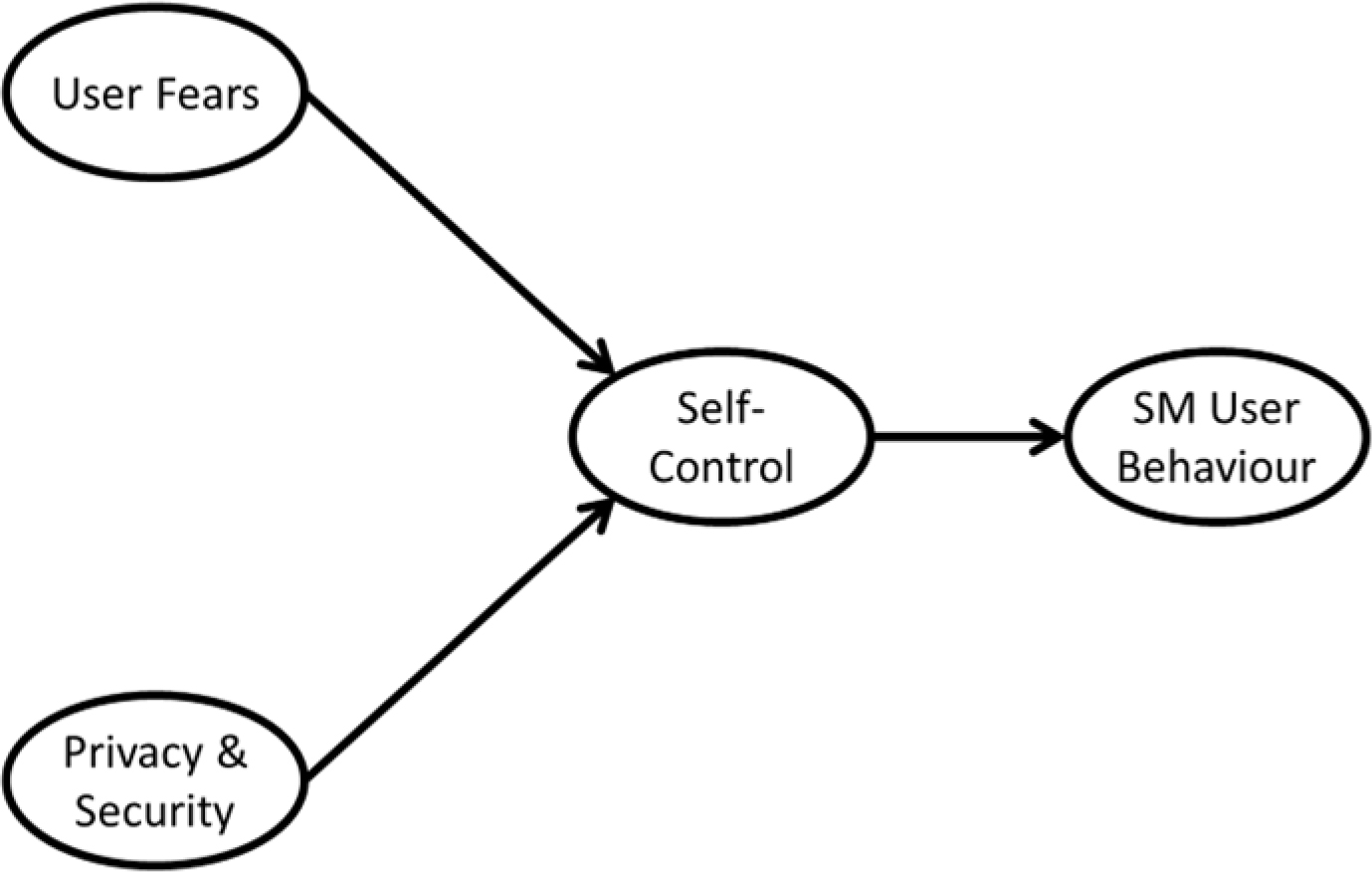
This research studies social media user fears, privacy and security concerns, and their effect on social media behaviour. It also studies the role of self-control on social media behaviour. The study is conducted in three stages; initially, four research constructs of user fears, privacy and security concerns, self-control, and social media behaviour were developed;-and tested for validity and reliability using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA). Then, hypothetical relations affecting user behaviour are tested with Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). Lastly, mediation analysis is conducted to study the role of self-control on user behaviour due to user fears and privacy-security concerns. Analysis shows that self-control plays a vital mediation role in social media behaviour. Further, gender and usage frequency have a controlling relationship between user fear, self-control, and self-control with user behaviour. Social media users tend to self-control their behaviour due to social media fears and privacy-security concerns. User fears lead to the user's self-control tendency to affect their behaviour.
Similarly, privacy and security perceptions lead to self-control, which affects social media behaviour. Social media firms should understand users' self-controlling behaviour, fears, and privacy-security concerns and develop security solutions to resolve them. This research is different in that it statistically confirms the self-controlling behaviour of users of social media applications.
ABSTRACT
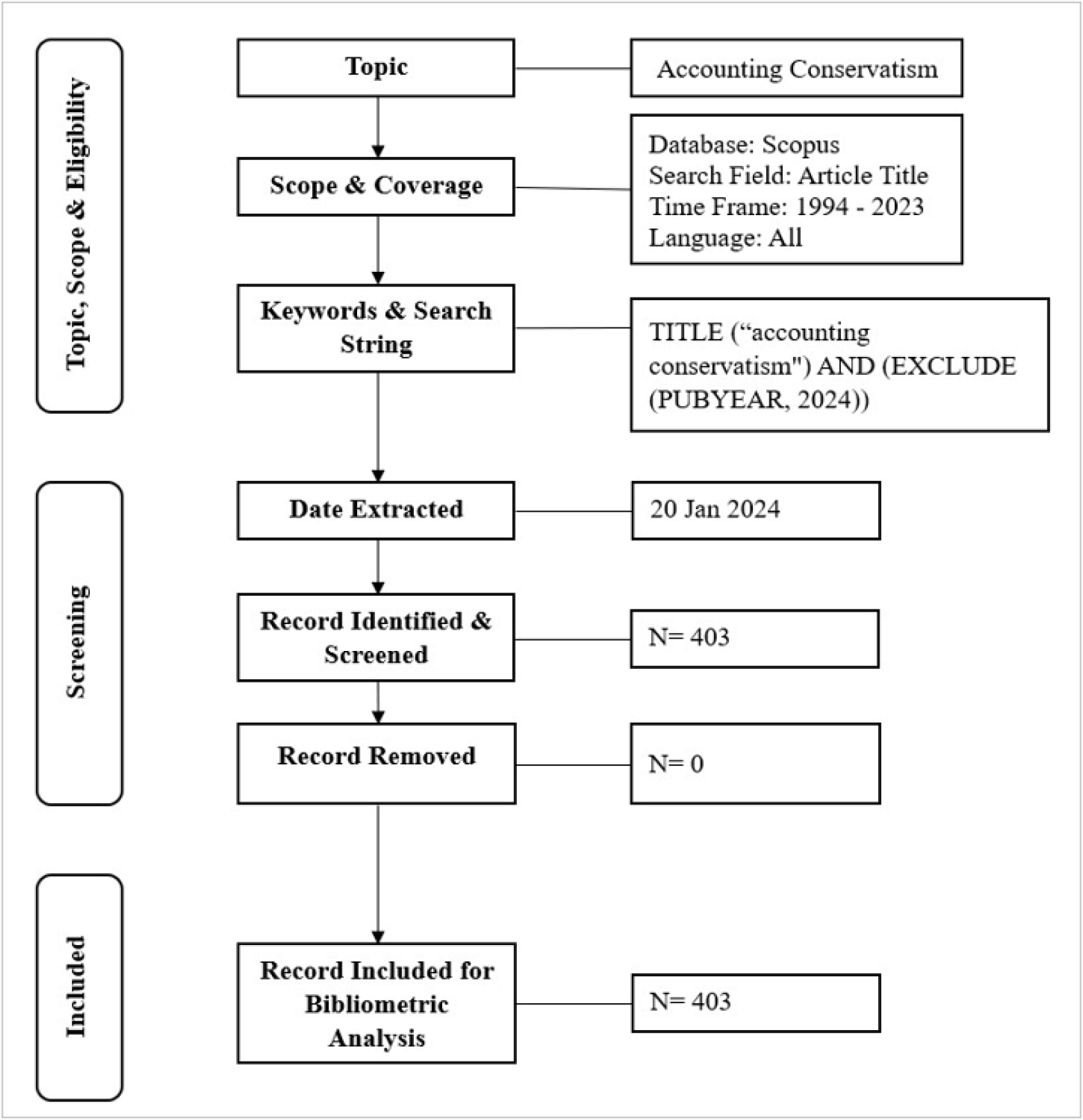
Accounting Conservatism (AC) is a fundamental concept in financial reporting, advocating for prudence in the recognition of financial information. Despite its critical role, there has been limited bibliometric analysis on AC research. This study addresses this gap by evaluating the evolution, current trends and future directions of AC research through a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. The research objectives are to identify prevailing research trends and citation patterns in the field of AC, explore key themes and influential works, assess the applicability of Lotka’s Law to AC research and propose future research directions based on the findings. By providing a detailed bibliometric analysis, this research offers valuable insights into the development of AC literature, highlights significant contributors and informs stakeholders about emerging trends and potential research gaps. The study employed a systematic approach to analyze 403 documents retrieved from the Scopus database using the search term "accounting conservatism." Data were cleaned and harmonized, and bibliometric analysis was conducted using tools including Microsoft Excel, Open Refine, VOSviewer and biblioMagika. VOSviewer was utilized to map research networks and visualize key themes. The analysis reveals a significant increase in AC publications since 2000, with 89% published as articles in English. Major contributors include the US, China, Australia, Canada and the UK. Influential works by Khan and Watts (2009) and Kim and Zhang (2016) were identified, alongside notable authors such as Anwer S. Ahmed and Gerald J. Lobo. Key themes include "Conditional Accounting Conservatism," "Information Asymmetry," and "Unconditional Accounting Conservatism." Lotka’s Law was applied, illustrating concentrated productivity among select authors, paralleling the principles of AC. This study enhances the understanding of AC research trends and provides practical implications for financial reporting and regulatory practices. It also suggests areas for future research, including the exploration of additional databases and emerging AC themes.
ABSTRACT
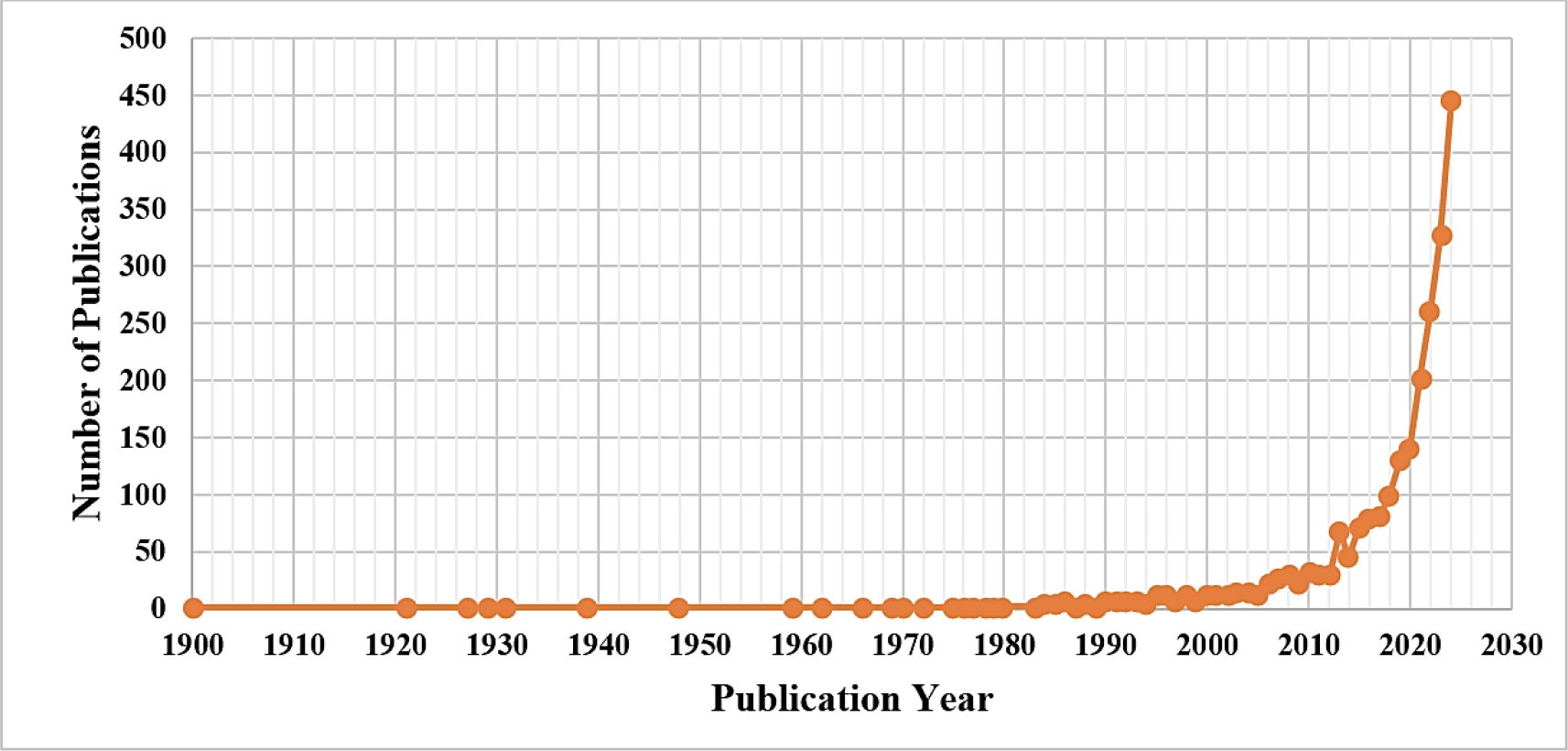
This research study focuses on appraising the relevant studies in anthropomorphism, i.e., humanizing the non-human entities. Firstly, research data points from 2,316 publications were retrieved using the Scopus database as of December 2024. Secondly, the finest literature was reviewed using Theory-Context-Characteristics-Methods (TCCM) to understand the insights and prospects of anthropomorphism studies and find the gaps. Thirdly, quantitative analysis was conducted using multiple bibliometric data points consisting of prominent authors, keywords, subject areas, source titles, institutional and country affiliations, and citations until data retrieval. Finally, an attempt was made to showcase the interconnectedness among authors, author keywords, and affiliated countries using network analysis. Anthropomorphism studies took a great leap during the last five years, publishing approximately 60% of research studies. As a country, the United States of America (USA) emerged as a solitary leader with almost 30% of anthropomorphism research. The anthropomorphism studies were deliberated in different contexts apart from its origin in psychology, such as human-technology interaction, sociology, consumer behavior, and organizational behavior.
ABSTRACT
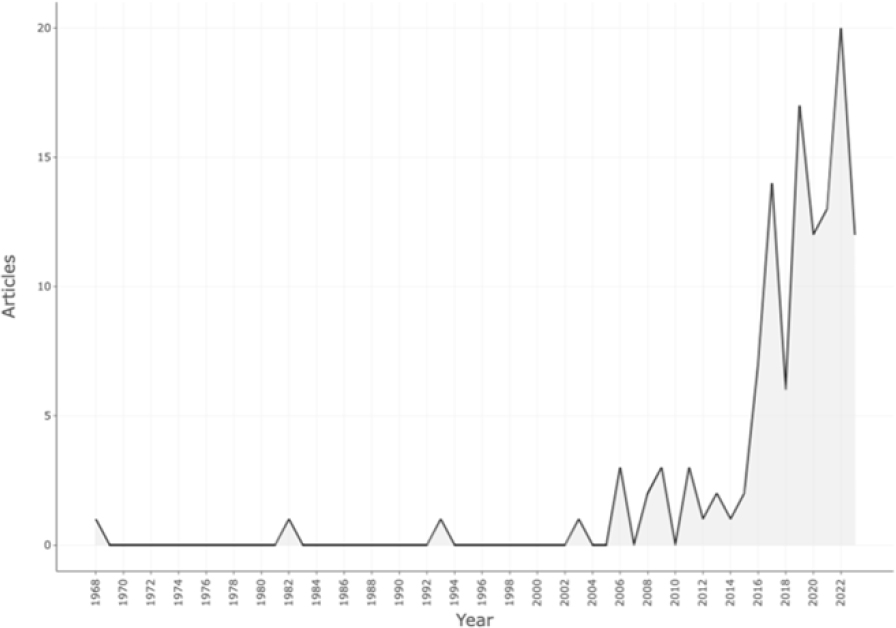
The growth of research in the field of public administration in Indonesia is substantial, but there is no comprehensive study that examines its evolution and future trajectory. Using a bibliometric approach, the purpose of this study is to investigate the thematic evolution and international collaboration in the field of public administration in Indonesia. To accomplish this objective, we analyzed a dataset comprised of publications from 50 leading public administration journals indexed in the Scopus database using a bibliometric technique. This method permits us to perform statistical analysis on bibliographic data in order to identify and define trends and patterns in research on public administration in Indonesia. The findings demonstrate significant shifts in research emphasis over time, with the emergence of new themes and the continued relevance of older ones. The collaboration map reveals significant collaboration with Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Malawi and Mozambique, among others, including Australia, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. Implications of this study include the significance of understanding the dynamics and evolution of public administration research, as well as the role of international collaboration in advancing knowledge in this field. This research also lays the groundwork for future studies to explore specific themes and collaboration dynamics in greater detail within the field of public administration in Indonesia.
ABSTRACT
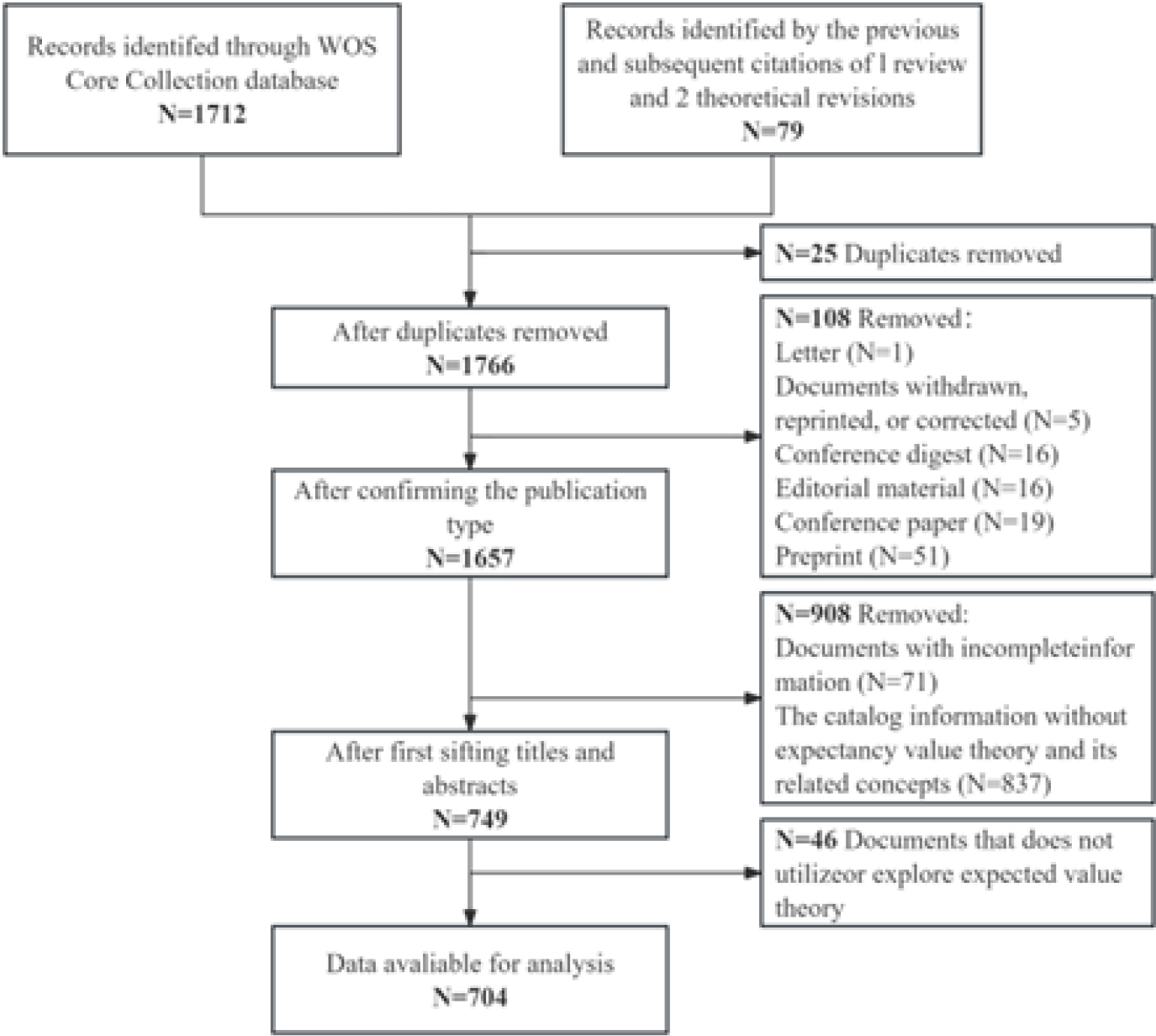
The Expectancy-Value Theory (EVT) has undergone rapid, which has guided many researches related to social cognition and learning motivation, and effectively addressing practical challenges across various scientific domains. However, a research gap exists regarding the quantification and visualization of the evolutionary trajectory of EVT. Therefore, this study utilizes 704 research articles related to EVT published between 1999 and 2023, this paper employs bibliometric and content analysis methods to delineate the developmental stages of EVT research. A framework is proposed, “theory-context-method” knowledge, to comparatively analyze the research content across different developmental stages. The main findings are: ①EVT research can be divided into three periods based on publication volume: the initial stage, slow development stage, and rapid publication stage; ②The developmental trajectory of EVT research from 1999 to 2023 is clear and can be divided into the instrumental stage (1999-2006), application exploration stage (2007-2016), and feedback optimization stage (2017-2023), each with distinct research themes and focal points; ③Current research focuses on the interdisciplinary and systematic study of EVT in fields such as education, psychology, and sociology, leading to a renewed understanding and further development of the theory itself; ④The research status and deficiencies of EVT are systematically discussed from the three aspects of the knowledge framework. This study reveals the research progress and trend systematically and intuitively on the EVT based on published literature, and to contribute to a deeper understanding and development of the theory itself.
ABSTRACT
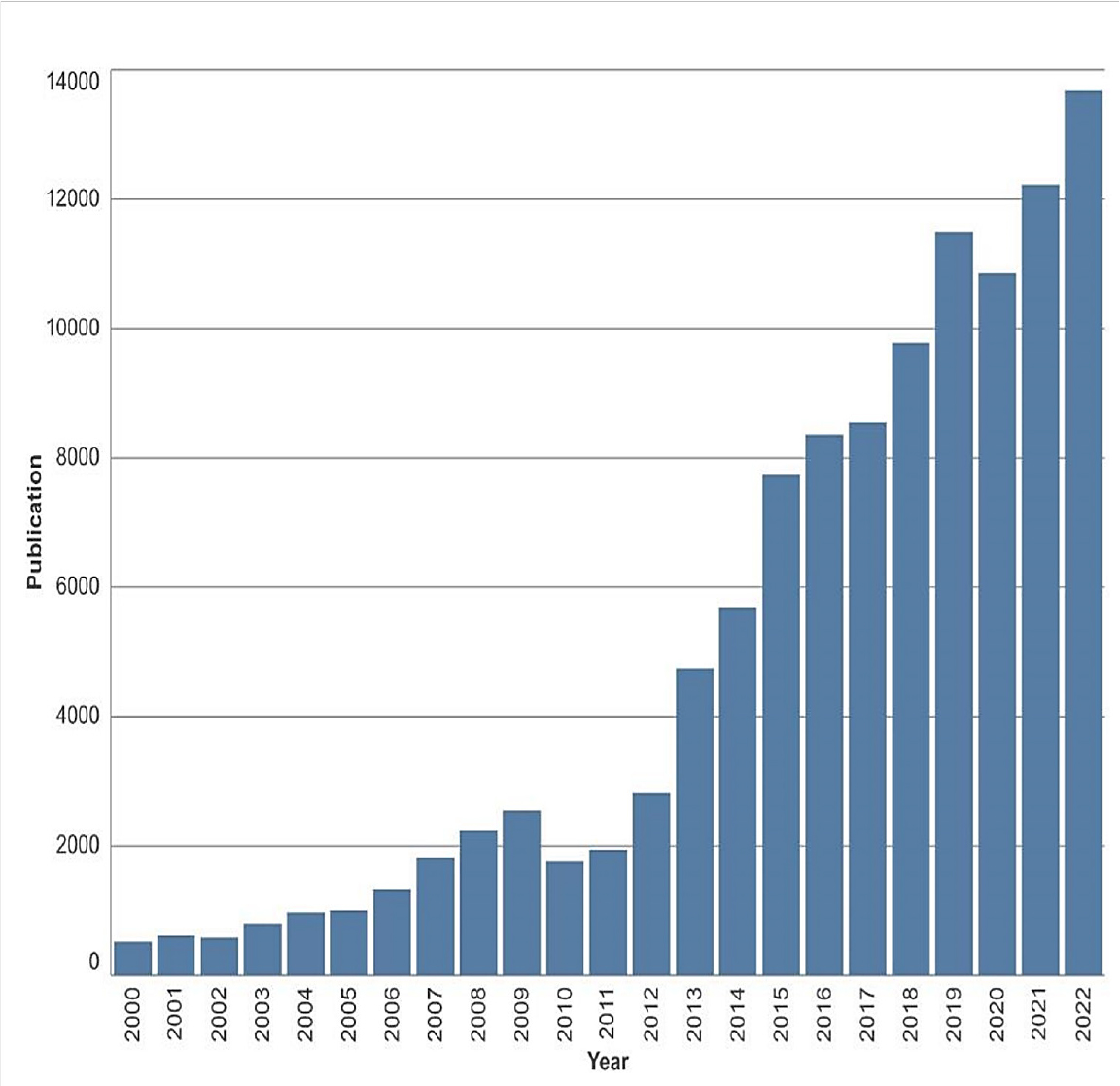
Industry 4.0 (IR4.0) has stimulated unprecedented interest in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, driving significant advances in computer science research within the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region over the last decade. This paper provides an overview of the research productivity, trends, and collaboration dynamics across 22 MEA countries, utilizing publication data from the Web of Science (WoS) database from 2000 to 2022. The findings reveal rapid growth in publications starting in 2013, with Saudi Arabia emerging as the leading contributor in the region. Computer science research in the MEA region is primarily associated with engineering and telecommunications, with key topics including artificial intelligence, theoretical derivations, and information science. Research trends have shifted from image processing to robotics, the Internet of Things, and machine learning. Collaboration among MEA countries has increased, with at least 50% of publications in the last decade involving non-MEA collaborators. The collaboration network exhibits a smallworld phenomenon, encouraging knowledge circulation and supporting the development of the MEA region in computer science research during the IR4.0 era.
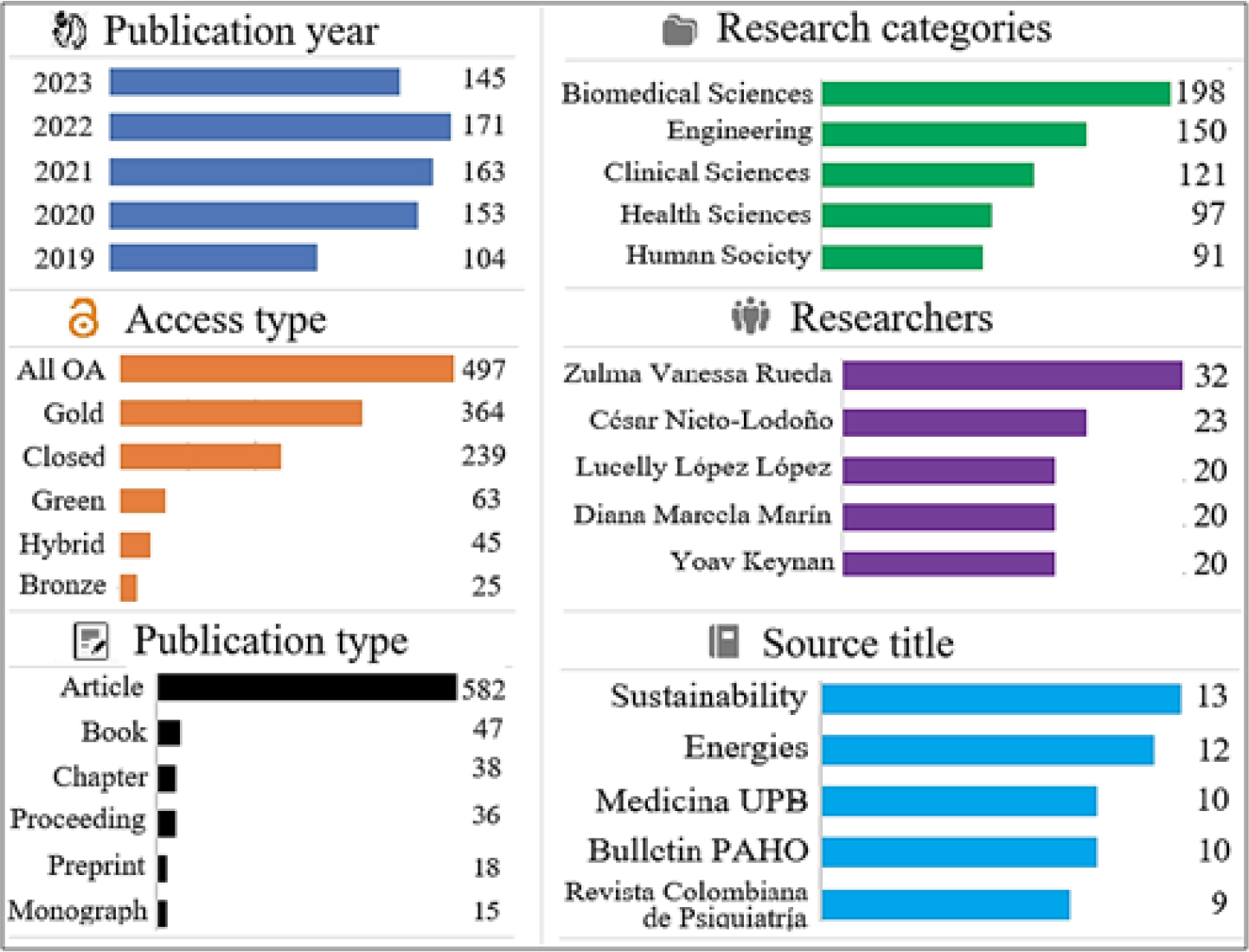
ABSTRACT
The 2030 Agenda and Sustainable Development Goals promote global resilience. Universities play a crucial role in their implementation through research and education. Recent studies analyze Sustainable Development Goals-related scientific production, but evaluating the accessibility and social impacts of these results remains lacking. The article aims to analyze the intersection between Sustainable Development Goals, open access, and social impact of science, based on an analysis of Pontifical Bolivarian University academic production in Colombia. A mixed-method approach is employed, combining quantitative and qualitative elements with scientometric techniques and data mining analysis, as well as big data from the perspective of Social Sciences. Pontifical Bolivarian University scientific production analysis reveals increased research activity, with most publications available in open access. Thematic focuses such as health, sustainable development, and energy are highlighted. Thematic diversity reflects a multidisciplinary approach, but there is low production in key areas of sustainable development. Social media attention highlights topics like health, equality, and energy. Open access shows a strong correlation with online attention, emphasizing its importance in amplifying research impact. Although closed research also receives online attention, especially from academics. Greater focus is needed on inclusive publishing strategies and social media dissemination to address global challenges.

ABSTRACT
Research Evaluation Systems (RESs) can be divided into "pre-performance or post-performance evaluation" or "retrospective or prospective evaluation". The Retrospective Research Evaluation Systems (RRESs), also known as Performance-based Research Funding Systems (PRFSs), are complex national systems designed to evaluate universities and research centers and allocate public funds based on their outputs and outcomes. This study compares the RRESs of the UK and Australia to gain a better understanding of the structure and components of these evaluation systems. A comparative study method was applied to look for similarities and differences between the RESs of selected countries. The two countries were chosen based on the criteria of transparency, access to credible documents, formality, comprehensiveness, flexibility, and management. Bereday’s four-step model consisting of description, interpretation, juxtaposition, and comparison of RESs was utilized for the data analysis. The results showed that two evaluation systems emphasize the components of human resources, finance and infrastructure in evaluation. Quantitative and qualitative approaches prevail in all two systems. In terms of the evaluation unit, the systems have almost the same structure, and the evaluation is done by specialized panels. The quality of research outputs is evaluated in two systems, and in the UK, the two elements of impact and research environment are also evaluated. In general, it can be said that the formation of national systems for research evaluation affects not only the quality of research, but also the purposefulness of research, scientific and technical progress of the country, and people’s lives. The unique aspect of this study is the comparison of the input, process, output, and impact components of the RRESs of the UK and Australia. The results can be beneficiary for managing and policymaking for research assessment units on micro/macro levels.
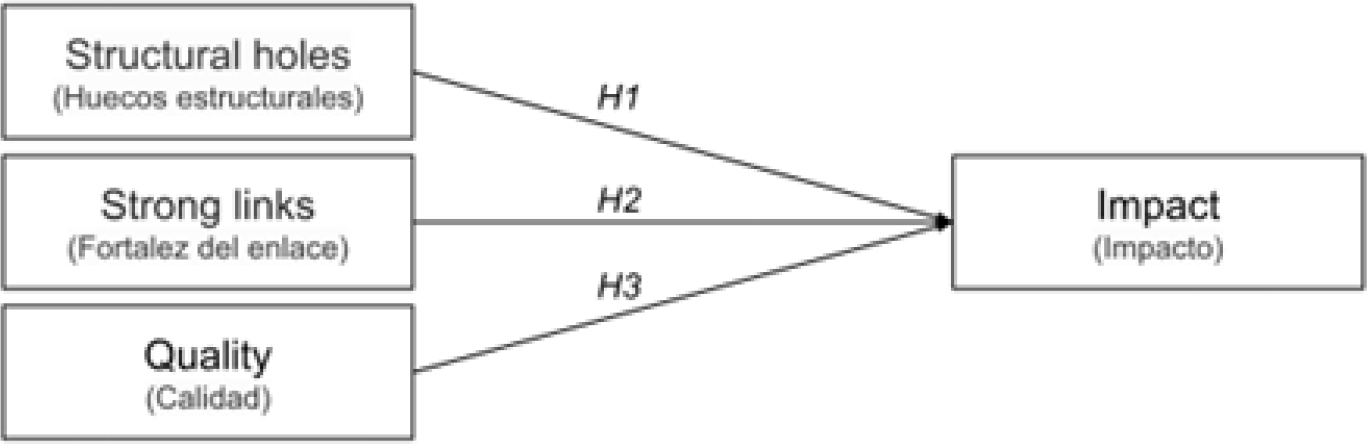
ABSTRACT
This research aims to analyze the correlation between performance measures and social network analysis in Occupational Positive Mental Health (OPMH) and Flourishing (FL) studies, assessing their global impact in recent decades. The methodology implemented was based on bibliometric analysis, using queries in Web of Science and Scopus databases, adapting the PRISMA methodology for data processing flow, employing bibliometric techniques, web scraping through Crossref, and employing descriptive, correlation, and regression analysis with Omnibus test and likelihood ratio test to measure significance levels. A total of 558 studies (WoS= 268) and (Scopus= 290) were processed, resulting in a total of (n=375) studies. The results reveal that among the collaboration networks, there were Nodes (N= 17,260) and Links (E= 94,772), while citation networks showed Nodes (N= 555) and Links (E= 1,151). Furthermore, a high correlation was found between the variables examined (structural holes, link strength, and quality) and the impact of research conducted in recent years in the fields of OPMH and FL. In conclusion, performance measures and collaborative social network analysis are correlated, enhancing understanding of unstructured information in mental health and other domains. Researchers with strong collaborative and multidisciplinary networks can enhance their impact by producing high-quality research, particularly in innovative areas like OPMH and FL.
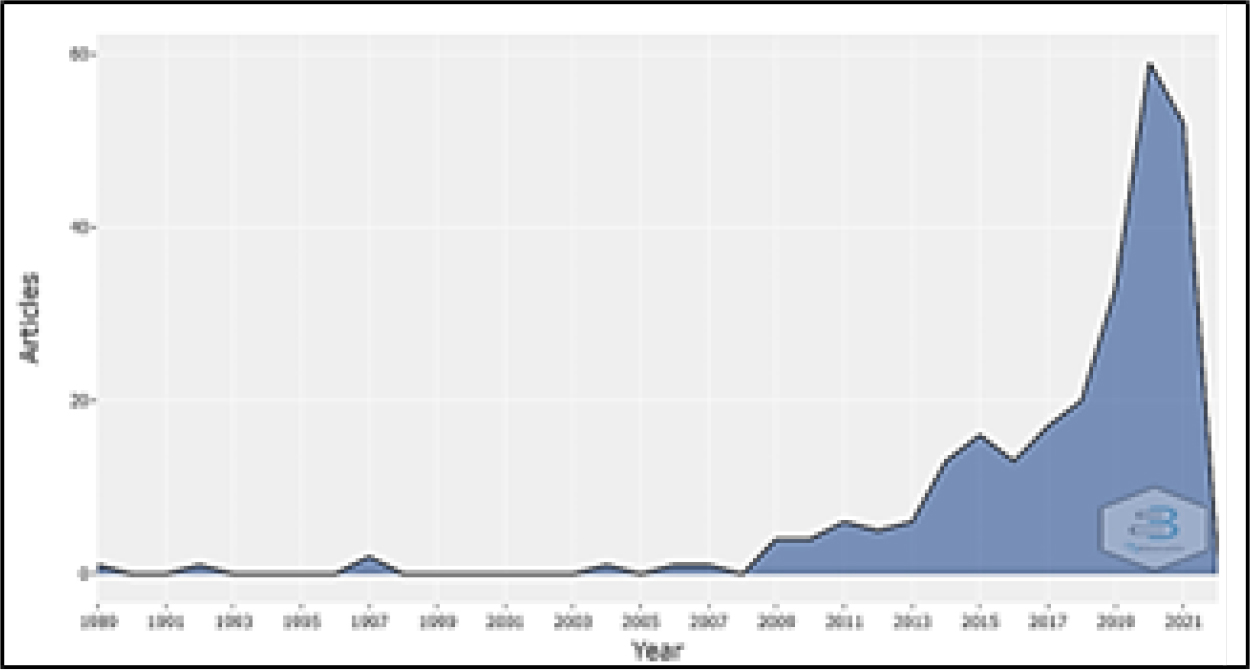
ABSTRACT
In response to the growing importance of critical thinking, particularly in academic writing instruction, this study aims to thoroughly investigate a specific writing genre within the broader literature on critical thinking. Additionally, it seeks to identify research opportunities and validate scientific inquiry. Our research provides a comprehensive examination of critical thinking tendencies in academic writings spanning from 1989 to 2021, utilizing data sourced from Bibliometrix, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis tool. We assess bibliometric indicators by applying VOSviewer and Biblioshiny software to shed light on trends and patterns in critical thinking research. Our findings show a significant growth in research interest focused on critical thinking within academic literature over the past three decades, particularly in contentious issues. Moreover, analysis of keyword correlations, geographical distributions, and institutional affiliations suggests that Asian countries are at the forefront of critical thinking and argumentative writing research, with prominent affiliations dispersed throughout the region. By uncovering critical, cutting-edge research themes, this study equips future scholars and practitioners with valuable insights into the evolution of critical thinking inquiries, especially within academic writing contexts. Moreover, it paves the way for developing empirical projects and highlights potential practical implications for advancing critical thinking education in academic settings. This research contributes to a deeper understanding of the dynamics of critical thinking in academic discourse and underscores the need for continued scholarly attention to this crucial aspect of education.
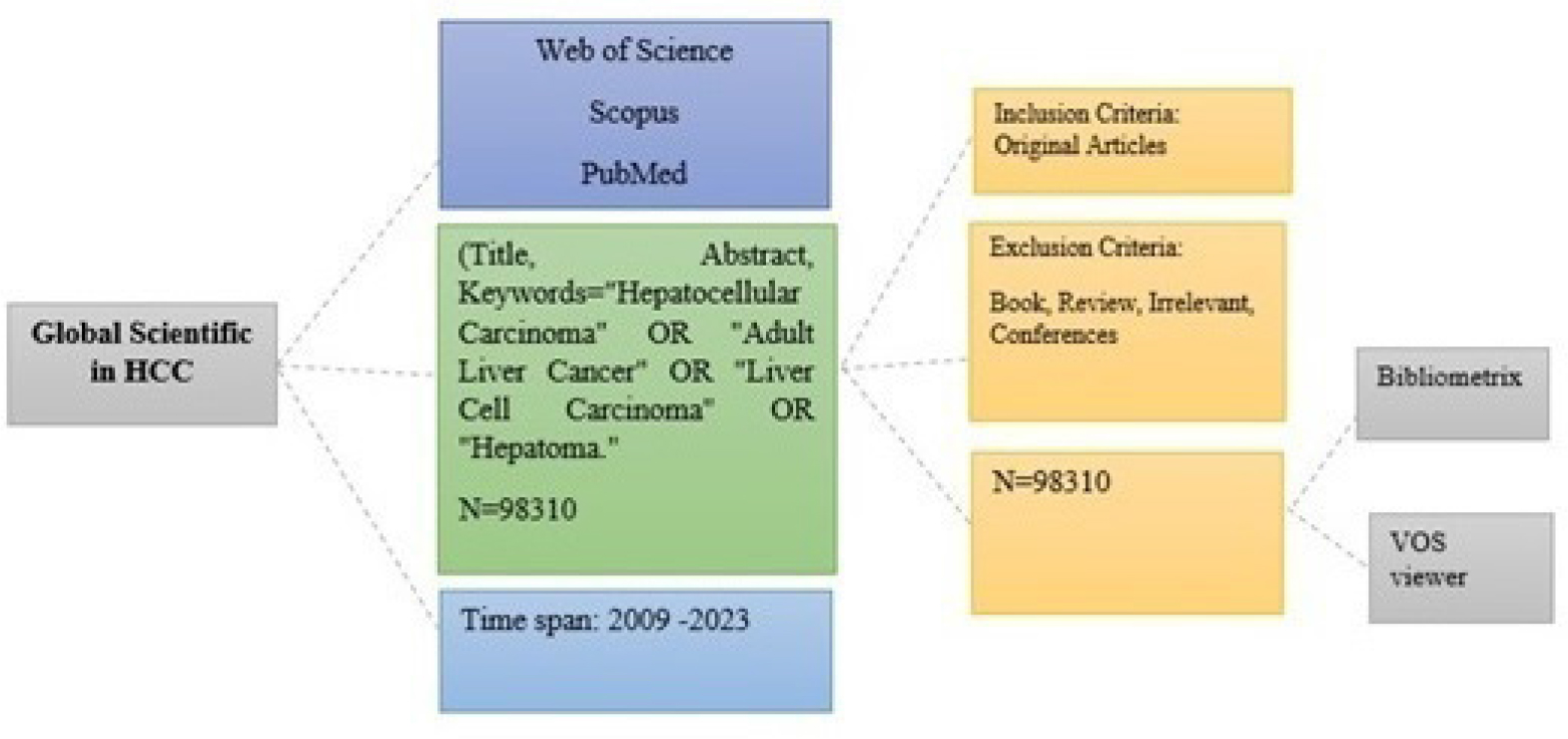
Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), the predominant primary histological subtype of liver malignancy, arises in the context of chronic liver disease. This study aims to construct a scientific map, conduct structural analysis, examine evolutionary trends, and identify emerging trends in the corpus of published research on HCC.
Materials and Methods
This descriptive survey employs scientometric analysis, using bibliographic records obtained from the Web of Science (WOS) to recognize the core documents central to research topics in the field.
Results
A total of 98,310 documents, all of which exclusively consist of journal articles, were extracted. Key words frequently associated with hepatocellular carcinoma include "hepatocellular carcinoma," "cirrhosis," "survival," and "management."
Conclusion
The results of the present study establish a framework delineating the evolution of key research themes in HCC over time, illustrating how researchers have responded to various milestones in its development. Identifying the most efficient methods, with the least prescribed dose yet the most therapeutic impact, remains of paramount importance.
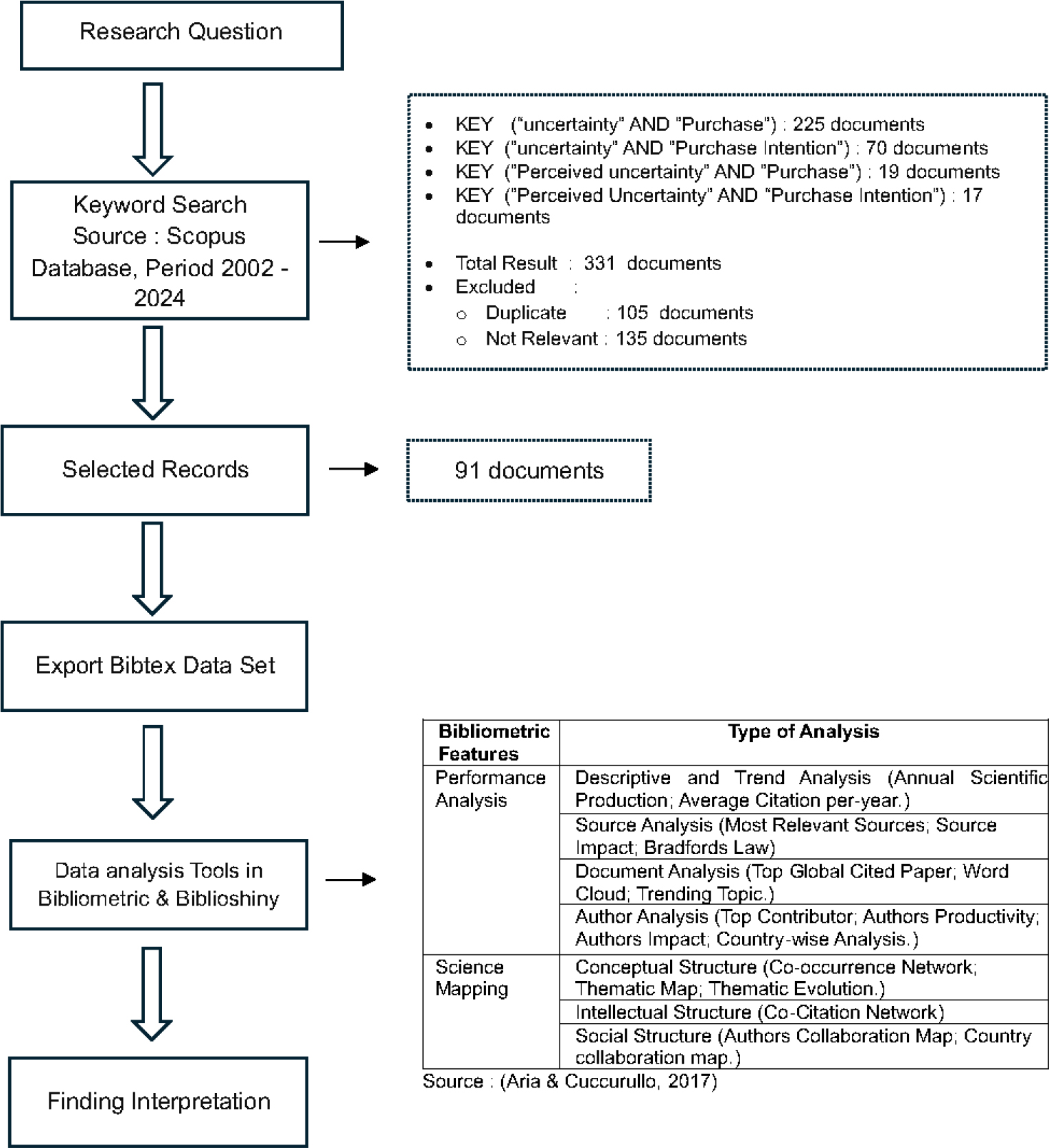
ABSTRACT
This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between perceived uncertainty and purchase intention through bibliometric analysis. The method used was a bibliometric analysis, assessing relevant literature from the Scopus database between 2002 and 2024. Data was collected using the keywords perceived uncertainty and purchase intention, and analyzed with Biblioshiny and Vos Viewer software. This research is novel as it is the first bibliometric study conducted on this relationship. The main findings include: first, an annual growth rate of 11.57% in publications, indicating increasing academic interest, with an average of 20.13 citations per document. Second, source analysis revealed that key literature came from psychology, marketing, information systems, and economics, with journals like Frontiers in Psychology having significant influence. Third, the terms perceived uncertainty and purchase intention have been the focal points of recent research. Fourth, scholarly mapping showed a strong international collaboration network, with the US, China, and the UK playing dominant roles. Fifth, terms like consumer trust and purchase intention appeared with higher density, suggesting their central role in related research, while variables like "brand loyalty" and "perceived value" appeared with lower density. Sixth, the Uncertainty Reduction Theory dominated with 11 publications. This research offered valuable insights for academics and opens opportunities for further research on contextual factors influencing this relationship. The practical relevance of this study including businesses can use AI to manage consumer uncertainty, enhance trust, and improve purchase intentions, emphasizing uncertainty management's role in shaping behavior and driving competitive advantages.
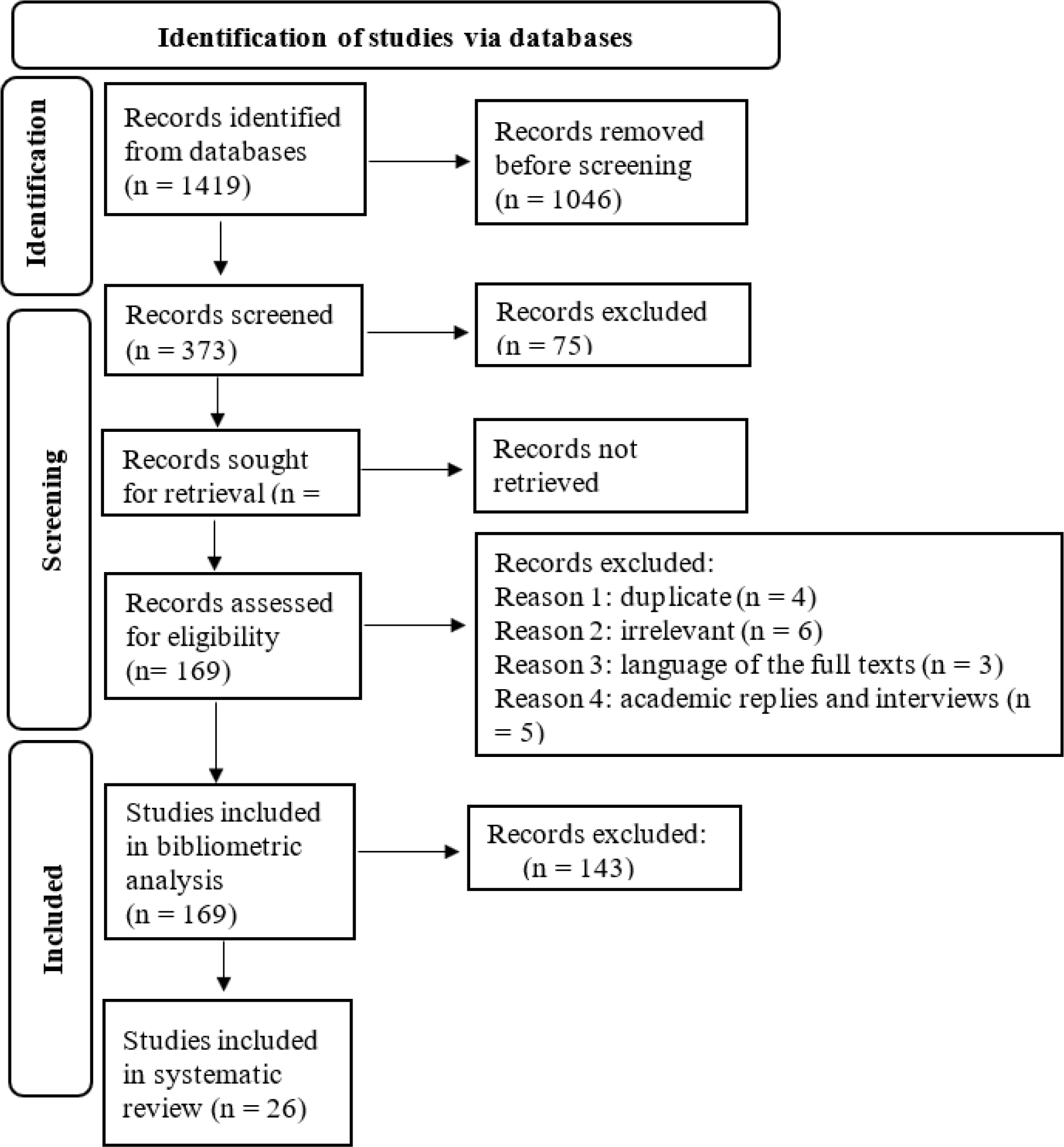
ABSTRACT
The academic contributions of Bruno Latour are significant and must be explored. Today, the contemporary tools, such as bibliometric analysis and systematic review provide great opportunity to do so. Findings, using these tools, help understand, for example, the hotspots and trends in research that translated Latour’s scholarly contributions. Latour’s research publications peaked in 2016, with the highest of twenty-five social sciences publications, spread in twenty-six countries. The three-field plot and co-word occurrence map illustrate his emphasis on Actor-Network Theory (ANT). The diverse applicability of Latourian ANT has an interdisciplinary impact in science and technology studies, ecology, and contemporary global issues. Latour’s oeuvre is also applied in Indian context. In providing counter-arguments on the criticisms of Latour, we delineate that his scholarship has brought a paradigm shift, especially in scientific epistemology. This is why our research will be useful for social scientists across social contexts.
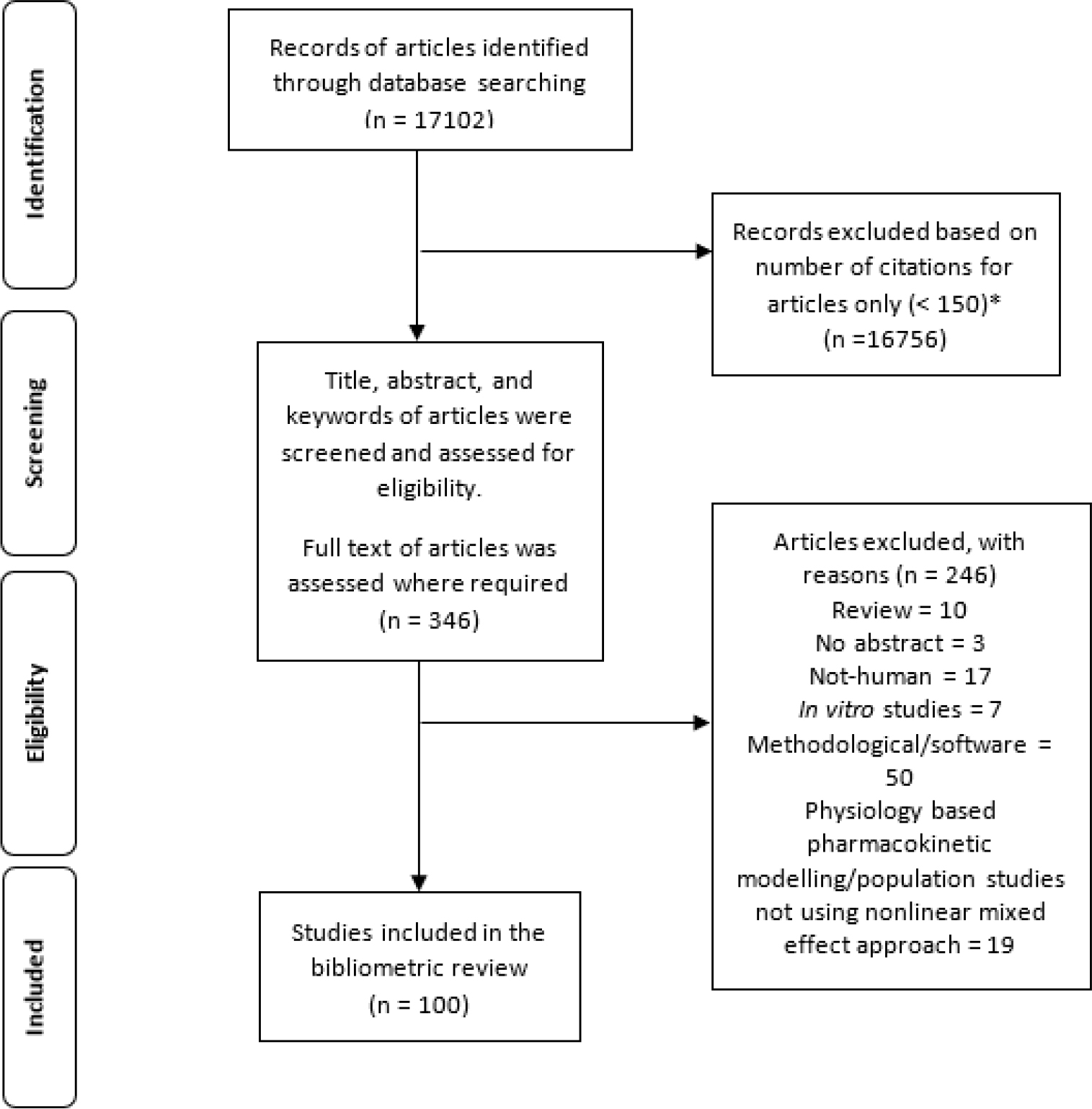
ABSTRACT
Population pharmacokinetic and/or pharmacodynamic [PK(/PD)] modelling has become more popular in drug development and academic research. However, there are no reports exploring the research trends in this area. To explore the (research) trends of most cited articles on PK(/PD) modelling, we bibliometrically analysed the most cited articles (n=100) extracted from the Scopus online database from inception (1964-2021) and again in the recent years (2015-2021) using VOSviewer v1.6.15 and Publish or Perish v8 software. Information such as ATC/drug class, model type, software used, studied population, authors’ institutions, journals, collaborations between countries, and funding sources was extracted and compared. Majority of the studies (65%) described in the 100 most cited articles were population PK modelling studies, with the proportion of the population PKPD modelling studies increasing over time (from 30 to 43%). A large percentage of the impactful articles (43%) were published by top five journals, analysed adult data (84%) and used NONMEM® (80%), which has not changed much over time. Most of the impactful articles studied chemotherapeutic and immunomodulating (33%), anti-infective (29%), and central nervous system (22%) ATC class of drugs, with articles analysing immunosuppressant drug class increasing the most over time (from 10% to 18%). In conclusion, we used a bibliometric approach and investigated research trends in top 100 most cited articles involving PK (/PD) modelling. Apart from the changes mentioned above most other metrics that we compared remained relatively unchanged over time.
